Professor Seo Jung-Hwa's Team Clarifies Electronic Structure in New Metal-Polymer Materials

- Published in "Advanced Functional Materials," a top 5% journal in the field of materials.
- Physical and chemical characterization of interfacial layers based on metal ion selectivity for efficient interfacial layer selectivity
A research team led by Proffessor Seo Jung-Hwa of the Department of Physics (Department of Intelligent Semiconductors) at University of Seoul(President Won Yongkul), has developed a metal ion-based polymer electrolyte material and successfully characterized the electronic structure of the material based on metal ion selectivity.

The research, conducted in collaboration with Dr. Park Suhyung’s research team at KIST and Professor Bright Walker's research team at Kyung Hee University, synthesized metal ion-doped polymer electrolytes and used photoelectron spectroscopy to reveal the properties and electronic structure of the new hybrid materials.
Interfacial control materials are materials that control the movement of electrons or holes between the semiconductor, the active layer of optoelectronic devices, and the electrode, and play a role in balancing the contact imbalance between the semiconductor and the electrode.
To ensure the performance and stability of semiconductor devices, it is very important to develop interface control materials that resolve the imbalance between the active layer and the electrode and facilitate the movement of electrons and holes.
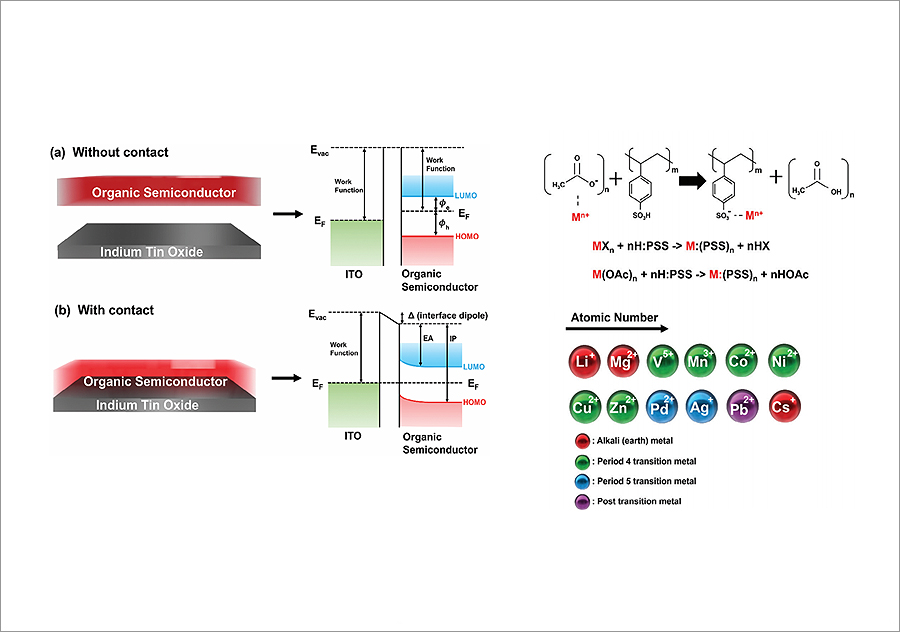
Dr. Walker's group successfully synthesized 15 types of metal ion-based polyelectrolytes as interfacial control materials, and Dr. Park Soo-Hyung team and Professor Seo Jung-Hwa's team adopted X-ray and ultraviolet spectroscopy techniques based on photoelectric effect to study the electronic structure of different types of metal ions, and as a result, clearly identified their role as interfacial control materials.
They developed Metal:PSS by replacing the PEDOT part of PEDOT:PSS, a conductive polymer widely used in optoelectronic devices such as OLEDs and solar cells, with metal ions, and studied various metal ions such as alkali metals (Li, Cs), Alkali Earth Metal (Mg), 4th period transition metals (V, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn), 5th period transition metals (Ag, Pd), and post-transition metals (Pb).
In the case of alkali metals and alkali earth metal, the work function of the electrode tended to decrease overall, showing the potential as an electron transport layer, and in the case of 4th period transition metals and 5th period transition metals, the work function of the electrode increased, and in particular, the increase in the work function of Cu and Ag was noticeable, showing the potential as a hole transport layer.
The results of the study were published online on January 24 in Wiley's top 5% journal in the field of materials, Advanced Functional Materials (Impact factor: 19.924), a prestigious international journal, with the title "Photoelectron Spectroscopic Study of the Interfacial Electronic Structures of Metal-Ion Containing Polyelectrolytes on ITO substrates".
This research was supported by Mid-career Researchers Program and Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by Ministry of Education